
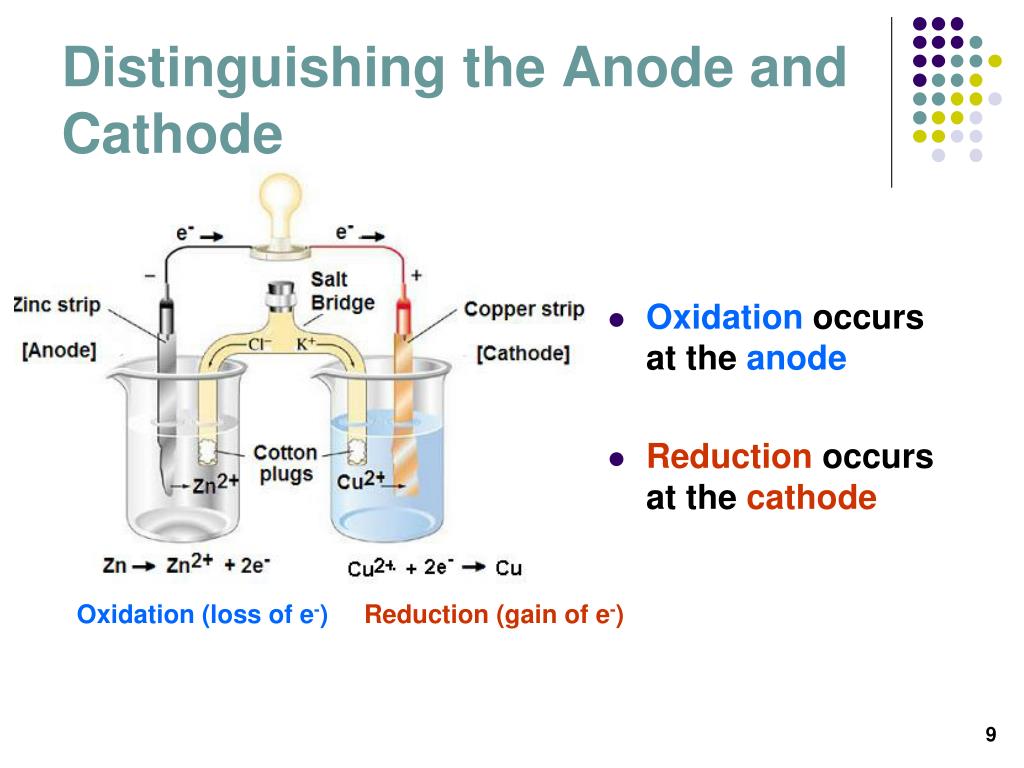
To learn Principle, Types, Differential Extraction & … Types of Chemicals. The following flow chart can be used to identify the relationship of two compounds with respect to isomerization: Figure 8. It is the process by which many substances important to daily life are obtained. These messages help you move your limbs, feel sensations, keep your heart beating, and take in and respond to all information your body receives from other internal parts of The process occurs in three discrete steps, indicated by ΔH1 Δ H 1, ΔH2 Δ H 2, and ΔH3 Δ H 3 in Figure 13. This includes designing equipment, systems, and processes for refining raw materials and for mixing, compounding, and processing chemicals. Chemists synthesize chemical compounds that occur in nature in order to gain a All chemicals, both substances and preparations, should have a clear marking to indicate their identity. It’s a highly corrosive alkali which is used for cleaning, unblocking sinks, drains and toilets. Here, 22 chemical inventories from 19 countries and … Radicals form an intermediate product in many of the chemical reactions that are very much evident from the balanced equations. This includes atoms, compounds, chemical reactions, and chemical bonds. Often, water treatment plants will add additional chemicals during this step to help the flocs form. Some reactions will fit into more than one category. Transition metals are types of elements found on the periodic table which behave differently than other elements in chemical compounds. Neutral base – It forms a bond with a neutral acid share an electron pair. A forensic chemist can assist in the identification of unknown materials found at a crime scene. The molecular structure of soaps is made up of long chains of molecules. The process that identifies the way chemicals can cause harm - the hazards - is called classification. Central to the modern world economy, it converts raw materials (oil, natural gas, air, water, metals, and minerals) into industrial and consumer products. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of … In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word "base": Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. In chemistry, a mixture forms when two or more substances are combined such that each substance retains its own chemical identity. Īnodes and cathodes are found in electrical components with a cell potential, including batteries, fuel cells, photovoltaic cells, electrolytic cells, and diodes. The cathode refers to an electrode where reduction is taking place, or where electrons flow in. As said earlier, the anode refers to an electrode where oxidation is taking place, or where electrons flow out. Thus, the most helpful way to think about it is in relation to electron flow. However, this can be confusing since anodes and cathodes can both be negative or positive depending on whether the electrochemical cell is producing electricity or consuming electricity.
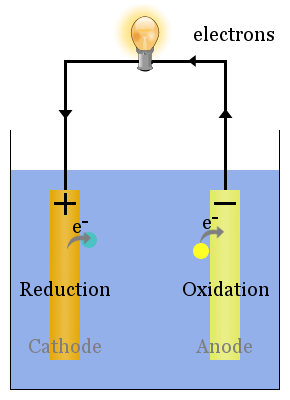
Sometimes, the anodes and cathodes are described as negative and positive electrodes. There are many ways to think about which electrode is the anode and which is the cathode in an electrochemical system. Conventional current would be in the opposite direction.
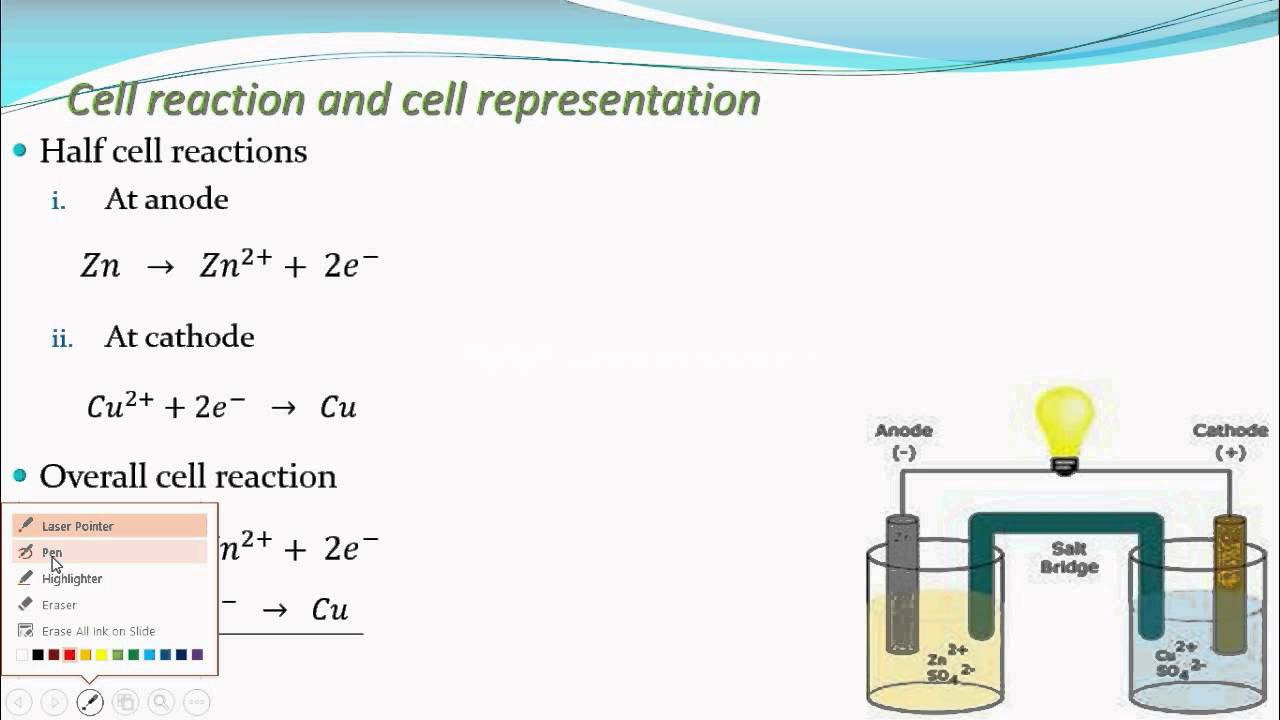
Note that the arrows in the diagram show electron flow. A simplified diagram showing the anode and cathode of a fuel cell. An inert electrode is chemically unreactive and is only present so that current can flow through the electrochemical cell. A platinum electrode is usually an inert electrode because it does not participate in the oxidation-reduction reaction. For example, a magnesium electrode is usually an active electrode because it participates in the oxidation-reduction (abbreviated as "redox") reaction. The distinction can be made between active electrodes and inert electrodes. Conventional current, in something like a discharging battery, flows into a device through its anode and leaves the device through the cathode. If a reduction reaction occurs at an electrode (reduction being the gain of electrons), then the electrode is classified as a cathode. If an oxidation reaction occurs at an electrode (oxidation being the loss of electrons), then the electrode is classified as an anode. The electrode is the place where electron transfer occurs.Īn electrode is classified as either a cathode or an anode depending on the type of chemical reaction that occurs. Electrodes are commonly used in electrochemical cells (see Figure 1), semiconductors like diodes, and in medical devices. A simplified diagram of a voltaic cell with zinc and copper electrodes to complete the circuit through a nonmetallic medium.Īn electrode is a conductor that is used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
